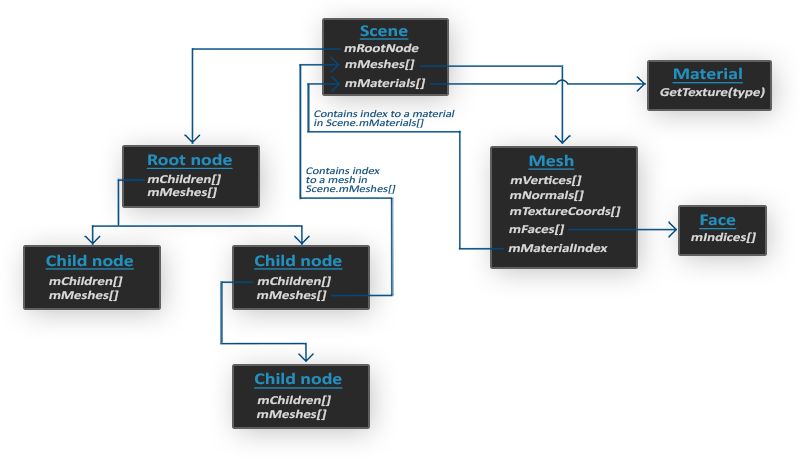
由于不同的文件格式有它自己的模型数据,需要对不同的模型格式进行不同的解析,Assimp库帮我们把这些模型格式抽象为一个特点的数据结构方便我们使用格式如下
通过文件nanosuit.obj来解释下这个图
# Blender v2.64 (sub 0) OBJ File: 'nanosuit.blend'
# www.blender.org
mtllib nanosuit.mtl
o Visor
v 0.320384 14.057541 0.507779
v 0.385196 13.984534 0.445066
v 0.416643 14.114325 0.462461
[...]
o Legs
v 1.899165 2.317634 -0.120600
v 1.903005 2.477843 -0.148509
v 1.899165 2.518403 -0.160526
v 1.970218 2.609661 -0.259889
[...]
o hands
v -3.554696 8.314335 1.450770
v -3.537413 8.306223 1.449854
v -3.512448 8.289999 1.458094
[...]
o Arms
v 3.658015 9.133632 1.108368
v 3.652269 9.133632 1.125763
v 3.667592 9.190415 1.074494
[...]
o Helmet
v 0.169514 13.749290 0.552182
v 0.214883 13.879080 0.523343
v 0.182237 13.911528 0.565000
[...]
o Body
v 1.413312 11.769991 -1.458770
v 1.418113 11.761879 -1.422149
v 1.420994 11.607754 -1.503631
[...]
o Lights
v 0.519383 14.098101 0.399747
v 0.474254 14.073765 0.435453
意思这个模型有7个局部。
通过Assimp库的 importer.ReadFile方法
void loadModel(string const &path) {
// read file via ASSIMP
Assimp::Importer importer;
const aiScene* scene = importer.ReadFile(path, aiProcess_Triangulate | aiProcess_FlipUVs | aiProcess_CalcTangentSpace);
// check for errors
if(!scene || scene->mFlags & AI_SCENE_FLAGS_INCOMPLETE || !scene->mRootNode) // if is Not Zero
{
cout << "ERROR::ASSIMP:: " << importer.GetErrorString() << endl;
return;
}
// retrieve the directory path of the filepath
directory = path.substr(0, path.find_last_of('/'));
// process ASSIMP's root node recursively
processNode(scene->mRootNode, scene);
}
(lldb) p *scene
(const aiScene) $19 = {
mFlags = 0
mRootNode = 0x00000001022f0c00
mNumMeshes = 7
mMeshes = 0x0000000101cdede0
mNumMaterials = 7
mMaterials = 0x0000000101cdee20
mNumAnimations = 0
mAnimations = 0x0000000000000000
mNumTextures = 0
mTextures = 0x0000000000000000
mNumLights = 0
mLights = 0x0000000000000000
mNumCameras = 0
mCameras = 0x0000000000000000
mMetaData = 0x0000000000000000
mPrivate = 0x0000000101c3ec40
}mRootNode也就是上图中的mRootNode,地址为0x00000001022f0c00mMeshes这里存放着我们场景中的所有mesh(可以理解为组成身体各个部分)mMaterials这里存放着所以的纹理数据
现在要做的事情就是把存放在scene里面的数据转为我们的Mesh数据结构
下面来看下mRootNode
(lldb) p *(aiNode *)0x00000001022f0c00
(aiNode) $20 = {
mName = (length = 12, data = char [1024] @ 0x00007ffb4d55cc08)
mTransformation = (a1 = 1, a2 = 0, a3 = 0, a4 = 0, b1 = 0, b2 = 1, b3 = 0, b4 = 0, c1 = 0, c2 = 0, c3 = 1, c4 = 0, d1 = 0, d2 = 0, d3 = 0, d4 = 1)
mParent = 0x0000000000000000
mNumChildren = 7
mChildren = 0x0000000101d8c7e0
mNumMeshes = 0
mMeshes = 0x0000000000000000
mMetaData = 0x0000000000000000
}- 由于
mNumMeshes == 0,所以mRootNode没有Mesh,按照上图需要查看children
- 可以看出为我们的
Visor实体在mMesh[]的索引值为0; Legs实体在mMesh[]的索引值为1;
先看自己的mesh索引,没有再看子节点的。
确实在mMesh[]中的0和1处找到了数据
以mMesh[1]也就是Legs为例
(lldb) p (aiVector3D *)0x0000000113d95000
(aiVector3D *) $51 = 0x0000000113d95000
(lldb) p *(aiVector3D *) $51
(aiVector3D) $52 = (x = 1.89916492, y = 2.31763411, z = -0.1206)
(lldb) p *(aiVector3D *) ($51 + 1)
(aiVector3D) $53 = (x = 1.903005, y = 2.47784305, z = -0.148508996)
(lldb) p *(aiVector3D *) ($51 + 2)
(aiVector3D) $54 = (x = 1.89916492, y = 2.51840305, z = -0.160526007)
(lldb)
可以和上面的.obj文件对比是一样的。
所以整个结构类似下面的
.
├── Material[] 存放场景中所有材质,数组
├── mMesh[] 存放着场景中所以的模型数据,
│ ├── mesh1
│ │ ├── mTextureCoords 纹理坐标
│ │ ├── normal 法向量
│ │ ├── vertex 顶点
│ │ └── ...其他
│ ├── mesh2
│ │ ├── mTextureCoords 纹理坐标
│ │ ├── normal 法向量
│ │ ├── vertex 顶点
│ │ └── ...其他
│ └── ... 其他的mesh
└── mRootNode
├── mChildren[]
└── mMesh[]
所以在将aiMesh转成Mesh的写法会是下面这样
void processNode(aiNode *node, const aiScene *scene)
{
// process each mesh located at the current node
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < node->mNumMeshes; i++)
{
// the node object only contains indices to index the actual objects in the scene.
// the scene contains all the data, node is just to keep stuff organized (like relations between nodes).
aiMesh* mesh = scene->mMeshes[node->mMeshes[i]];
meshes.push_back(processMesh(mesh, scene));
}
// after we've processed all of the meshes (if any) we then recursively process each of the children nodes
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < node->mNumChildren; i++)
{
processNode(node->mChildren[i], scene);
}
}那么,三者的关系很简单,Model就是讲asMesh转变成Mesh的中介者。